The piston is equivalent to the central component of the car engine and plays an extremely important role when the engine starts. This article will explore the piston’s meaning, working principle, function, and classification in depth to help you better understand this engine part.
What is an Engine piston?
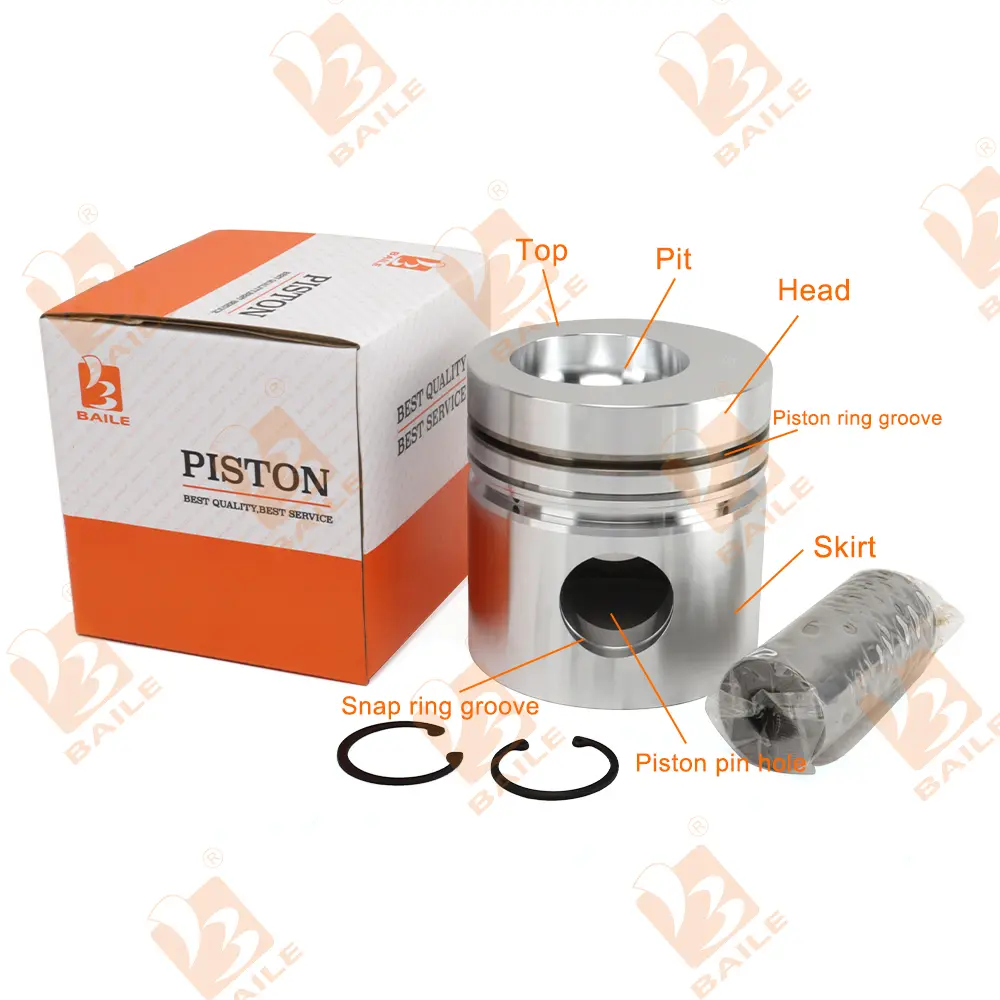
The piston is a reciprocating part in the cylinder block of a car engine. Its basic structure can be divided into the top, head, and skirt. The top is the main part of the combustion chamber, and its shape is related to the selected combustion chamber form; the head is equipped with piston rings to prevent high-temperature and high-pressure gas from entering the crankcase and prevent oil from entering the combustion chamber; the skirt plays a role in guiding the piston to reciprocate in the cylinder and withstand side pressure.
The basic structure of the piston can be divided into the top, the head, and the skirt.
 Piston top
Piston top
The top of the piston is the main part of the combustion chamber, and its shape is related to the selected combustion chamber form. For example, gasoline engines use more flat-top pistons because the heat absorption area is small. Diesel engine pistons must adapt to the requirements of diesel engine mixture combustion according to their specific shape, position, and size, so they have various pits on the top.
The top of the piston is in direct contact with high-temperature and high-pressure gas, so it is usually made of high-temperature and wear-resistant materials, such as aluminum alloy or steel.
Piston head
The piston head is generally the part above the piston pin seat. The piston head is equipped with piston rings to prevent high-temperature and high-pressure gas from entering the crankcase, and also to prevent engine oil from entering the combustion chamber and affecting the piston movement.In addition, most of the heat absorbed by the top of the piston must also be transferred to the cylinder through the piston head and then conducted out through the cooling medium.
Piston skirt
The part below the piston ring groove is called the piston skirt, which guides the piston to reciprocate in the cylinder and bears the side pressure. At the same time, the shape and size design of the piston skirt helps to keep the piston stable in the cylinder and reduce wear and noise.
How does the piston work?
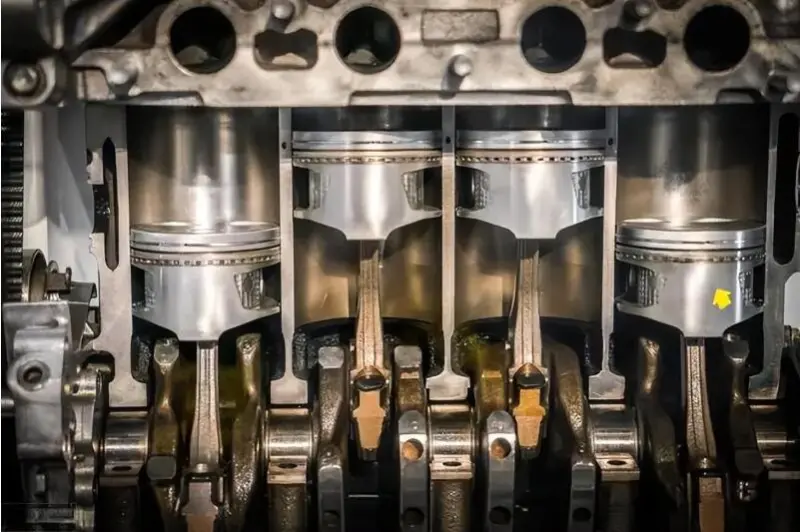
The working principle of the piston is relatively intuitive but crucial. In the four strokes of the engine (intake, compression, power, exhaust), the piston plays a core role.
Intake stroke: The piston moves downward from the top of the cylinder to make room for the fuel and air mixture (gasoline engine) or pure air (diesel engine) to enter the cylinder.
Compression stroke: As the piston moves upward, the gas in the cylinder is compressed, and the pressure and temperature increase accordingly.
Power stroke:In a gasoline engine, the spark plug ignites the fuel mixture, generating explosive force to push the piston downward; in a diesel engine, high-pressure diesel is sprayed into the high-temperature and high-pressure cylinder and ignites spontaneously, also pushing the piston downward. During this process, the piston is subjected to huge gas pressure, and this pressure is transmitted to the connecting rod through the piston pin, which in turn drives the crankshaft to rotate and generate power.
Exhaust stroke: The piston moves upward again to discharge the exhaust gas in the cylinder.
Simply put: The piston moves up and down in the combustion chamber as the crankshaft rotates, and this movement is transmitted to the crankshaft through the connecting rod and converted into rotational power. Through the precise reciprocating motion of the piston, the engine can generate electricity efficiently.
The role of the piston
The role of the engine piston is crucial and undertakes multiple key functions. The following are the main functions of the engine piston:
![]() Sealing the cylinder: The piston fits tightly with the cylinder wall to form a sealed working space. This sealing ensures that the gas in the cylinder will not leak into the crankcase, and also prevents the oil from entering the combustion chamber, thereby ensuring the normal operation and high efficiency of the engine.
Sealing the cylinder: The piston fits tightly with the cylinder wall to form a sealed working space. This sealing ensures that the gas in the cylinder will not leak into the crankcase, and also prevents the oil from entering the combustion chamber, thereby ensuring the normal operation and high efficiency of the engine.
![]() Withstand gas pressure: During the power stroke of the engine, the top of the piston directly bears the high-temperature and high-pressure gas pressure generated in the combustion chamber.
Withstand gas pressure: During the power stroke of the engine, the top of the piston directly bears the high-temperature and high-pressure gas pressure generated in the combustion chamber.
![]() Transmit power: The piston is connected to the connecting rod through the piston pin. When the piston is subjected to gas pressure, it converts this pressure into mechanical energy and transmits it to the crankshaft through the connecting rod. The rotational motion of the crankshaft ultimately drives the car’s transmission system and wheels, allowing the car to drive.
Transmit power: The piston is connected to the connecting rod through the piston pin. When the piston is subjected to gas pressure, it converts this pressure into mechanical energy and transmits it to the crankshaft through the connecting rod. The rotational motion of the crankshaft ultimately drives the car’s transmission system and wheels, allowing the car to drive.
![]() Composition of the combustion chamber: The top of the piston, the cylinder head, and the cylinder wall together form the combustion chamber of the engine.
Composition of the combustion chamber: The top of the piston, the cylinder head, and the cylinder wall together form the combustion chamber of the engine.
![]() Guide and support: The piston reciprocates in the cylinder, and its skirt plays a guiding and supporting role. The design of the piston skirt ensures that the piston can maintain the correct posture during movement and maintain an appropriate gap with the cylinder wall, thereby reducing friction and wear.
Guide and support: The piston reciprocates in the cylinder, and its skirt plays a guiding and supporting role. The design of the piston skirt ensures that the piston can maintain the correct posture during movement and maintain an appropriate gap with the cylinder wall, thereby reducing friction and wear.
![]() Heat conduction: The piston also has the task of transferring the heat generated by combustion to the cooling system. The piston is usually made of materials with good thermal conductivity, such as aluminum alloy, to ensure that the heat can be dissipated in time to prevent the engine from overheating.
Heat conduction: The piston also has the task of transferring the heat generated by combustion to the cooling system. The piston is usually made of materials with good thermal conductivity, such as aluminum alloy, to ensure that the heat can be dissipated in time to prevent the engine from overheating.
In summary, the sealing, pressure bearing capacity, power transmission efficiency, and thermal conductivity of the engine piston have an important impact on the performance and life of the engine. Therefore, in the design and manufacturing process of the engine, the material selection, structural design, and manufacturing process of the piston have been strictly considered and optimized.
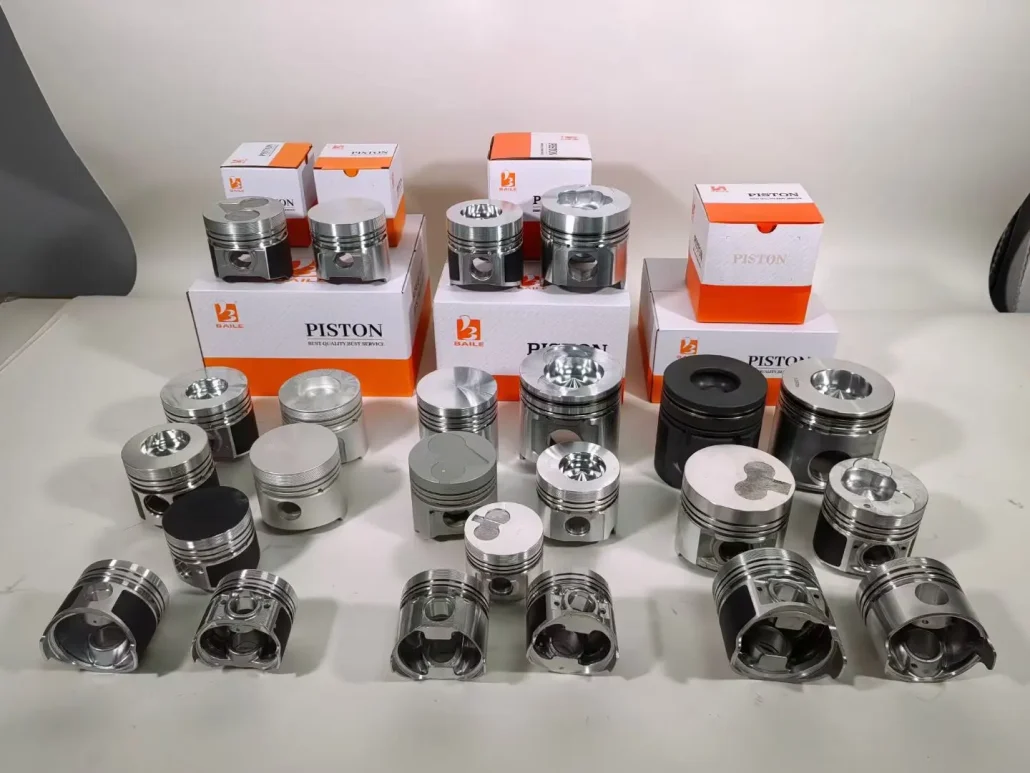


Piston type
- The materials used to make pistons are divided into cast iron pistons, steel pistons, aluminum alloy pistons, and combined pistons;
- The fuels used by pistons are divided into gasoline engine pistons, diesel engine pistons, and natural gas pistons;
- The working state of pistons is divided into two categories: non-pressurized pistons and pressurized pistons;
- The process for making piston blanks is divided into gravity casting pistons, extrusion casting pistons, and forged pistons.
There are many ways to distinguish pistons, each of which is based on its specific usage requirements and working conditions. When choosing a piston, you should consider factors such as engine type, power, fuel type, and working environment.


